
Omeprazole is a commonly prescribed medication for acid reflux and stomach ulcers. However, recent research has shown a potential link between omeprazole and thrombocytopenia, a condition characterized by low platelet count.
If you are experiencing unexplained bruises, nosebleeds, or excessive bleeding, it may be important to discuss your medication regimen with your healthcare provider. Stay informed and prioritize your health.
Understanding Omeprazole Thrombocytopenia
Omeprazole, a commonly prescribed proton pump inhibitor (PPI), is used to treat various conditions such as acid reflux, ulcers, and heartburn. It works by reducing the production of stomach acid, providing relief to patients suffering from these conditions.
However, in some cases, omeprazole may lead to thrombocytopenia, a condition characterized by a low platelet count in the blood. Platelets are crucial for the blood clotting process, and a decrease in their count can result in excessive bleeding and bruising.
How Does Omeprazole Cause Thrombocytopenia?
The exact mechanism by which omeprazole induces thrombocytopenia is not fully understood. Some studies suggest that omeprazole may affect the bone marrow’s ability to produce platelets, leading to a decrease in their count. Additionally, it is believed that omeprazole may trigger an immune response that targets platelets, further exacerbating the condition.
Thrombocytopenia: Key Facts
Thrombocytopenia is a medical condition characterized by a low platelet count in the blood. Platelets are essential for blood clotting and preventing excessive bleeding. When the platelet count is below normal levels, individuals may experience increased bruising, bleeding gums, and prolonged bleeding from minor injuries.
Thrombocytopenia can have various causes, including underlying health conditions, medications, and autoimmune disorders. It is crucial to monitor platelet levels regularly and seek medical attention if symptoms of thrombocytopenia arise.
Connection Between Omeprazole and Thrombocytopenia
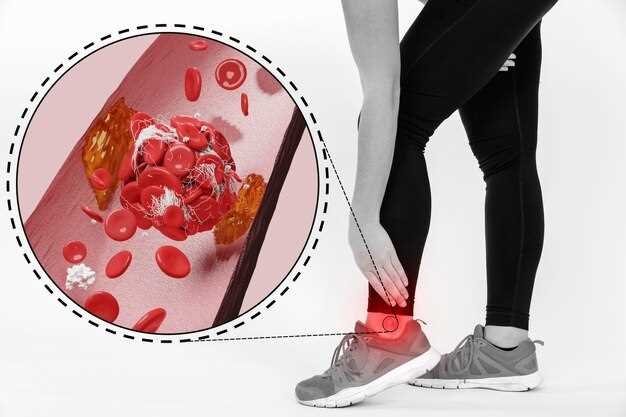
Thrombocytopenia, a condition characterized by low platelet count, has been reported in some patients who have taken Omeprazole. Platelets are crucial for blood clotting, and a decreased count can lead to issues with clotting and increased risk of bleeding.
Omeprazole, a proton pump inhibitor commonly used to treat gastrointestinal issues, has been linked to cases of thrombocytopenia. While the exact mechanism is not fully understood, it is believed that Omeprazole may interfere with the production or function of platelets in some individuals.
Connection Between Omeprazole and Thrombocytopenia
Omeprazole, a commonly prescribed proton pump inhibitor (PPI), has been linked to the development of thrombocytopenia in some patients. Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by a low platelet count in the blood, which can lead to abnormal bleeding and bruising.
Research suggests that omeprazole may inhibit the absorption of vitamin B12 in the body, which could potentially lead to the development of thrombocytopenia. Vitamin B12 plays a crucial role in the production of platelets, the cells responsible for blood clotting.
How Does Omeprazole Cause Thrombocytopenia?
- Omeprazole may interfere with the absorption of vitamin B12, which is essential for platelet production.
- Low levels of vitamin B12 can lead to decreased platelet counts, increasing the risk of thrombocytopenia.
- Patients taking omeprazole long-term or in high doses may be at a higher risk of developing thrombocytopenia.
It is important for patients taking omeprazole to be aware of the potential risk of thrombocytopenia and to consult their healthcare provider if they experience symptoms such as unexplained bruising, bleeding, or fatigue. Monitoring platelet counts regularly can help detect thrombocytopenia early and prevent complications.
Symptoms of Thrombocytopenia Caused by Omeprazole
Thrombocytopenia caused by Omeprazole can manifest in various symptoms that indicate a low platelet count in the blood. Some common symptoms include:
Bruising: Easy bruising or purpura may occur even with minor trauma due to decreased platelet levels.
Nosebleeds: Frequent or prolonged nosebleeds may be a sign of thrombocytopenia.
Excessive Bleeding: Bleeding gums, prolonged bleeding from cuts or injuries, and heavy menstrual bleeding can indicate a low platelet count.
Petechiae: Small, red or purple spots on the skin that result from minor blood vessel bleeding may be present.
Fatigue: General weakness, fatigue, and tiredness can be symptoms of thrombocytopenia-induced anemia.
If you experience any of these symptoms while taking Omeprazole, consult your healthcare provider for proper evaluation and management.
Treatment Options for Thrombocytopenia
When it comes to treating thrombocytopenia caused by Omeprazole, the main goal is to increase the platelet count and prevent bleeding complications. Here are some common treatment options:
| 1. Stopping Omeprazole: | One of the first steps in addressing Omeprazole-induced thrombocytopenia is to discontinue the use of Omeprazole. This can help the platelet count to recover over time. |
| 2. Medications: | In some cases, medications such as corticosteroids or intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) may be prescribed to help increase platelet production. |
| 3. Platelet Transfusions: | In severe cases of thrombocytopenia with a high risk of bleeding, platelet transfusions may be necessary to quickly raise the platelet count. |
| 4. Surgery: | In rare cases where other treatments are not effective, surgery to remove the spleen (splenectomy) may be considered to prevent platelet destruction. |
It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable treatment plan based on the severity of thrombocytopenia and individual health factors.
Prevention and Risk Management Strategies
In order to prevent thrombocytopenia associated with Omeprazole, it is important to follow some key strategies:
1. Regular Monitoring: Regular monitoring of platelet levels is essential for individuals taking Omeprazole. This helps in early detection of any drop in platelet count.
2. Consultation with Healthcare Provider: It is important to consult your healthcare provider if you notice any unusual symptoms such as spontaneous bruising or bleeding while taking Omeprazole.
3. Medication Review: Review your current medications with your healthcare provider to identify any potential interactions that could lead to thrombocytopenia.
4. Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate rest, can help in maintaining overall health and reducing the risk of complications.
5. Awareness of Symptoms: Educate yourself about the symptoms of thrombocytopenia so that you can seek medical help promptly if needed.
6. Avoid Self-medication: Do not self-prescribe Omeprazole or any other medications without consulting a healthcare professional.
By following these prevention and risk management strategies, individuals can reduce the likelihood of developing thrombocytopenia while using Omeprazole.
